PATHOLOGIES WE TREAT
Sarcoptic Mange (Scabies)
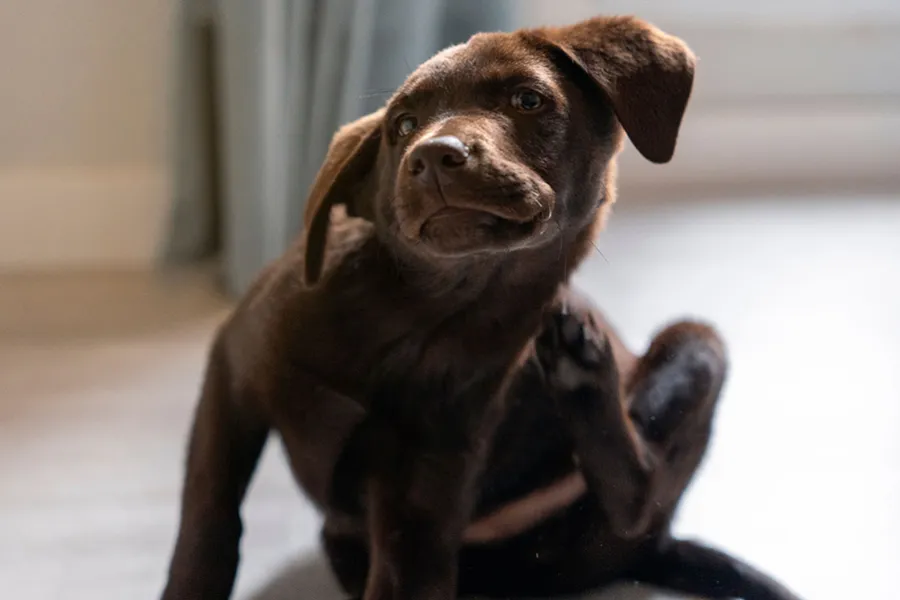

Introduction
Sarcoptic mange, also known as “scabies,” is a highly contagious skin disease caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis. It primarily affects dogs but can also infect cats and, in some cases, humans. This infestation causes extreme discomfort in pets and can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
Causes
Sarcoptic mange is caused by microscopic mites that burrow into the skin of the host to lay eggs and reproduce. This activity triggers intense itching and inflammation. The disease spreads easily through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated objects such as bedding and toys.
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of sarcoptic mange in dogs is intense itching (pruritus). As the mites feed and damage the skin, the dog experiences severe itching and scratching. Other common symptoms include:
- Hair loss (alopecia): Often around the ears, face, abdomen, and legs, resulting from scratching and biting.
- Crusts and wounds: Caused by intense scratching and biting of the affected areas.
- Red, inflamed skin (erythema): In affected areas.
- Secondary infections: Due to constant scratching and skin damage.
In severe cases, the mange can spread over the entire body, and the condition may become chronic if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing sarcoptic mange involves:
- Reviewing the clinical history.
- Observing characteristic symptoms, such as hair loss, crusts, and redness on the ears, face, abdomen, and legs.
- Performing skin scrapings, although mites may not always be detected.
- Ruling out other causes of itching, such as infections or allergies.
- Confirming the diagnosis by observing improvement after antiparasitic treatment.
Treatment
Treatment focuses on eliminating mites and relieving symptoms:
- Antiparasitics: Medications such as ivermectin, milbemycin, or selamectin are effective in eradicating the mites.
- Managing secondary infections: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections resulting from scratching wounds.
- Medicated baths: Help eliminate mites on the skin's surface and provide initial relief.
- Topical products:
- Skinnia Calm is essential for soothing irritated skin, maintaining hydration, and reducing discomfort, promoting rapid recovery.
- Skinnia Wounds aids in wound healing and prevents infections caused by scratching.
In severe cases, antihistamines or corticosteroids may be prescribed to control inflammation and itching.
Prevention
- Avoid contact with infected animals.
- Regularly disinfect the environment: Clean and disinfect bedding, toys, and other items frequently, as mites can survive outside the host for weeks.
- Preventive antiparasitics: Consult a veterinarian about regular treatments to prevent mite infestations.
- Routine check-ups: Early detection and treatment can prevent the disease from spreading.
Müller, G. H., Kirk, R. W., & Scott, D. W. (2012). Small Animal Dermatology (7th ed.). Saunders Elsevier.
Patel, A. & Forsythe, P. (2008). Saunders Solutions in Small Animal Practice: Veterinary Dermatology (1st edition). Saunders Elsevier.
Bornstein, S., Mörner, T., & Samuel, W. M. (2001). Sarcoptes scabiei and sarcoptic mange. Parasitic diseases of wild mammals, 107-119.
Curtis, C. F. (2012). Canine sarcoptic mange (sarcoptic acariasis, canine scabies). Companion animal, 17(8), 32-36.
Bioadhesive transparent gel indicated to moisturise, protect and soothe the dry skin of small animals.
Healing film forming gel indicated to protect and accelerate the natural healing process of the skin after surgery.