PATHOLOGIES WE TREAT
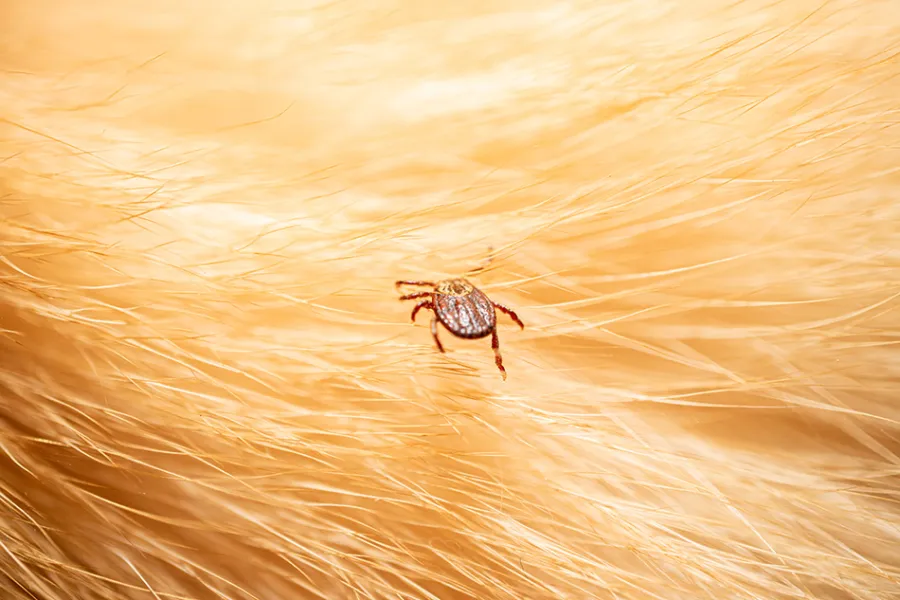
Ticks

Introduction
Ticks are arachnids that attach to the skin of animals to feed on their blood. Their presence on dogs and cats is more common in warm and humid weather. Besides being an annoyance to pets, ticks are vectors of various zoonotic diseases that can also impact human health.
Risk Factors
Ticks are commonly found in outdoor environments, especially wooded areas, tall grass, and shrubs. The following factors increase the risk of tick infestations:
- Outdoor exposure: Pets that spend a lot of time outdoors are more likely to encounter ticks.
- Warm, humid climate: Ticks thrive in warm and humid conditions, although in some regions, they can be active year-round.
- Lack of prevention: Pets without regular preventive treatments, such as spot-on applications, oral medications, or collars, are at higher risk.
- Long and dense coats: Ticks can hide more easily in thick fur, making detection more difficult.
Symptoms
Although ticks are small, their bites can lead to immediate and long-term symptoms, including:
- Excessive scratching or licking: Ticks can irritate the skin, causing pets to scratch or lick more than usual.
- Redness and swelling: Tick bites often result in inflamed, red areas, sometimes accompanied by rashes.
- Lethargy or loss of appetite: In severe infestations, tick bites can lead to anemia and weakness in pets.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a tick infestation typically involves a physical examination, focusing on areas like the ears, neck, armpits, and between the toes. If symptoms like itching, redness, lethargy, or appetite loss are present, the veterinarian may suspect a tick-borne disease. In these cases, blood tests can detect infections caused by Borrelia, Ehrlichia, Anaplasma, or Babesia.
Treatment
Treating ticks involves both removal and symptom management:
- Manual removal: Use tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull gently to ensure the entire tick is removed. Avoid squeezing the tick’s body to prevent infection.
- Topical relief: Products like Skinnia Calm can soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and promote the healing of tick bite sites.
Prevention
Preventing tick infestations is essential for safeguarding your pet’s health. Follow these steps:
- Use preventive products: Apply antiparasitic treatments, such as spot-on applications, oral medications, or collars, that protect against ticks for extended periods. Consult your veterinarian for the best option.
- Regular inspections: Check your pet’s coat frequently, especially after walks in wooded or grassy areas. Remove any ticks promptly.
- Avoid high-risk areas: During peak tick activity seasons, limit your pet’s access to areas with dense vegetation where ticks are common.
Medleau, L., & Hnilica, K. A. (2017). Small Animal Dermatology: A Color Atlas and Therapeutic Guide (4th ed.). St. Louis, Mo., Saunders Elsevier.
Jackson, H. A., Marsella, R., & British Small Animal Veterinary Association. (2012). BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dermatology (3rd ed.). British Small Animal Veterinary Association.
Scott, D. W., Miller, W. H., & Griffin, C. E. (2001). Muller and Kirk's Small Animal Dermatology (6th ed.). Elsevier.
Shaw, S. E., Day, M. J., Birtles, R. J., & Breitschwerdt, E. B. (2001). Tick-borne infectious diseases of dogs. Trends in parasitology, 17(2), 74-80.
Estrada-Peña, A., Bouattour, A. J. L. C., Camicas, J. L., & Walker, A. R. (2004). Ticks of domestic animals in the Mediterranean region. University of Zaragoza, Spain, 131.
Bioadhesive transparent gel indicated to moisturise, protect and soothe the dry skin of small animals.